Driving next-gen efficiency and productivity to the battery lifecycle
With soaring demand for batteries today, how can production keep pace? Learn why Vicor power dense modules are perfectly designed to meet today’s demands
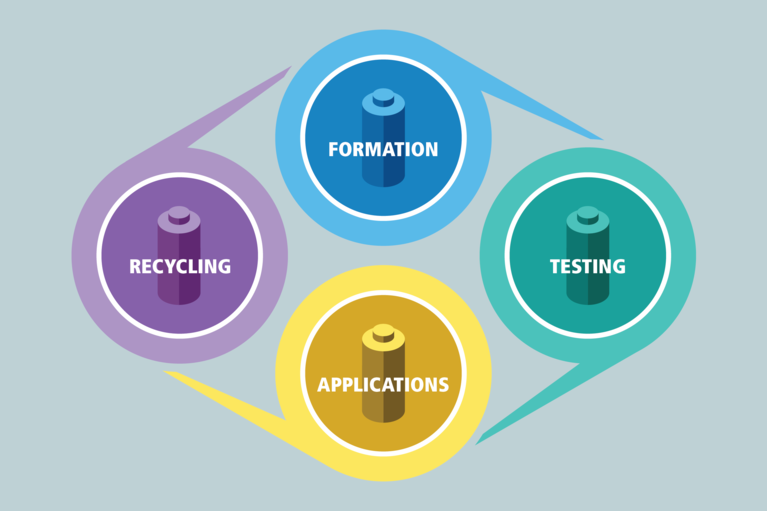
This handy reference of commonly used terms will help you navigate and understand the complex language of the battery formation and test industry.
Hydrogen retention by the hydrogen-absorbing Misch metal alloys of batteries’ negative electrodes.
The battery in which acid is used as electrolyte, e.g., lead-acid battery in which sulfuric acid is the electrolyte.
Electrode material which produces electrical energy during discharge from chemical energy stored during charge
A battery which employs alkaline aqueous solution for its electrolyte. The Nickel-cadmium battery as designed.
The average temperature of the battery's surrounding medium, typically air.
Unit expressing the capacity of a battery or cell. Ampere Hours are the product of a battery's or cell's discharge rate and discharge time. Usually measure in mAh (milli-Amps x hours).
Electrode where oxidation takes place during electro-chemical reaction. Negative electrode is the anode during discharge; positive electrode is the anode during charge.
Any battery composed of multiple cells.
two or more electrically connected cells in a series/parallel arrangement, designed to create the desired voltage/capacity. "Battery" is the common term for a single cell.
A battery cell with overall height less than its diameter. Button cells are manufactured with circular disc electrodes that are separated with a separator sheet
C designates the nominal capacity of the battery. The charge-discharge current is specified in terms of a multiple of C. For example, the 0.1 current for N-1300SC is equal to 1300 X 0.1 = 130mA.
Unit by which charge and discharge times are scaled. The capacity of NiCd batteries is commonly rated at 1C, meaning that a 10000mAh battery would be discharged at 10000mA for one hour.
This metallic element is the chemically-active material of the Nickel-cadmium battery's negative electrode. When the battery is charged, the negative electrode surface consists of cadmium. As the battery discharges, the cadmium progressively changes into cadmium hydroxide (CdOH2).
Active material used at the negative electrode of the nickel-cadmium cell.
A chemical compound in which the hydrogen atom as been replaced by the cadmium atom: (e.g.: 2HNO3 + Cd(OH)2 -> Cd(NO3)2 + 2H2O cadmium nitrate).
The electric energy content of a battery expressed in ampere hours. The energy is referenced to the discharge at a constant current for a measured period of time until a specified cut-off voltage is reached.
Electrode where reduction takes place during electro-chemical reaction. Positive electrode is the cathode during discharge; negative electrode is the cathode during charge.
Maximum amount of electrical current that can be withdrawn from a battery cell under specified conditions. Capacity is the product of discharge rate and discharge time (mAhr = mA x hrs); measured in milli-amp hours (mAh).
A correction factor applied to the rating of a battery if discharged under different C-rates from the one rated.
A cell is the basic electro-chemical unit which stores electrical energy or releases stored electrical energy
Cells within a battery pack that contain different capacity and voltage levels.
The discharging of a cell to a state of reversed polarity. Usually requires three or more cells for this to occur
Charge termination based on difference between ambient temperature and cell temperature
Charge termination based on change in temperature over time. This termination is meant to detect rapid temperature increases created just before a battery or cell reaches its full charge. Normal dT/dt is 1°C/minute.
The process of replenishing or replacing the electrical charge in a rechargeable cell or battery.
A cell's ability to store energy. Can be affected by temperature, charge rate, and state of charge.
Ratio of a cell's output during discharge to its input during charge. Ratio can be expressed in efficiency of capacity, nominal voltage, or power.
Current applied to a cell to restore its capacity. Charge rate is usually expressed in terms of the cell's C rate.
Residual capacity after a period of storage of a fully charged battery.
The capacity remaining in a cell or battery.
The type of cells which convert energy obtained by chemical reactions into electrical current. Most of the popularly used cells belong to this group.
A charge during which the current is maintained at a constant value. Sealed nickel-cadmium batteries are normally charged at a constant.
A charge during which the voltage across the battery terminals is maintained at a constant value. This method is not normally used for sealed nickel-cadmium cells or batteries.
A unit to measure the in-going charge and out-going discharge current of a battery. A coulomb is equal to the electricity transferred by a current of one ampere in one second. (The maximum energy a molecular weight of a chemical system can deliver is one Faraday of energy or 96,500 coulombs which is the equivalent of 26.8Ah of capacity).
A charger that keeps the charge current constant during the charge process but allows the voltage to fluctuate (typically used on NiCd and NiMH chargers).
The specified voltage at which a discharge of a cell or battery is considered finished (final voltage).
Battery sequence of a discharge followed by a recharge, or a charge followed by a discharge.
Number of cycles a cell can operate through, under specified conditions, before becoming nonfunctional.
A method of battery use involving repeated charging and discharging.
Cell with a circular cross-section and height greater than its diameter. Manufactured by winding electrodes spirally with a separator between them.
Application in which the cell or battery is successively and repeatedly charged, then completely and fully discharged.
Discharge of at least 80% of the rated capacity of a cell or battery.
Capacity removed from a battery as compared to its actual capacity. It is expressed in percentage
Detecting the voltage drop which indicates a cell is fully charged. See "negative Delta V (-ΔV)".
See "memory effect".
The ratio of a cell's or battery's electricity, usually expressed in terms of capacity, removed on discharge to its rated capacity.
An operation during which a battery delivers current to an external circuit by the conversion of chemical energy into electrical energy.
Capacity that can be discharged from a battery. The unit as Ah, (ampere-hour).
Rate at which electrical current is removed from a cell or battery, usually measured in milli-amperes (mA) or multiples of the C Rate
Voltage a battery's or cell's terminals during discharge.
Operating regime for a battery or cell, including charge and discharge rates, charge termination, depth of discharge, and time in rest mode.
Matrices of a battery or cell which provide the sites for the electro-chemical process to take place
Medium which provides the ion transport mechanism between a battery's or cell's electrodes. Potassium Hydroxide (KOH) is the electrolyte in NiMH batteries, for example.
The degree to which a separator retains electrolyte.
The voltage that indicates the end limit of discharge. This voltage is almost equivalent to capacity in practical use.
Heat absorption caused by a chemical reaction.
Overall amount of power a battery or cell can deliver over time. Product of the battery's or cell's voltage, discharge rate, and discharge time. Usually expressed in milli-Watt hours (mWhr) or mWhr = V x mA x hrs.
Ratio of a battery's or cell's energy to its weight or volume. Also called Power Density. See also "gravimetric energy density" and "volumetric energy density".
Commonly understood as one or more discharge cycles to one volt per cell with subsequent recharge. Used to maintain NiCd & NiMH batteries.
Release of heat caused by a chemical reaction
Rate of charging a cell or battery to full charge capacity in 2 1/2 hours or less.
The specified voltage at which a discharge of a battery is considered finished.
Similar to trickle charge. Compensates for the self-discharge on a SLA battery.
Matrix that stores active material in a battery's or cell's positive electrode.
The degree of mobility of gas through porous film, fabric or other plate-separating material.
The method to suppress hydrogen generation by recombining oxygen gas on the negative electrode, and making the negative electrode chemically discharged when oxygen gas is generated at the positive electrode at the end of charging.
Ratio of a battery's or cell's energy to its weight. Also called power density. Usually expressed in Watt-Hours per kilogram (Wh/kg).
Discharge at a comparatively high current rate in comparison with cell capacity.
The hour rate is associated with both discharging and charging the battery, and is expressed in terms of discharge time at its nominal capacity rating. "H-hou" represents the length of time it takes to discharge a battery, and "i" represents the rate of discharge.
International Electro-technical Commission, a non-profit, non-governmental international standards organization. Prepares and publishes international standards for all electrical, electronic, and related technologies.
An atom or a group of atoms charged either positively or negatively.
Used in terms of the battery's internal resistance.
Battery with internal circuit enabling some communication between the battery and user. Some batteries feature a capacity indicator only, others offer an external bus to interface with the equipment the battery powers and the intelligent charger.
Reaction where lithium ions are reversibly removed or inserted into a hose without a significant structural change taking place
Opposition or resistance of a battery or cell to an alternating current, usually 1000Hz. Internal resistance is the ohmic component of a battery's or cell's resistance to the flow of electrical current within the battery or cell.
Pressure within a sealed battery or cell caused by oxygen or hydrogen evolution
A space between closely set things, or between the parts which compose a body. A narrow chink; a crack, crevice, or hole
A drop in cell voltage or voltage of inter-cell conductor due to cell internal resistance.
The escape of electrolyte to the outer surface of the battery.
Dark blue, water-insoluble powder. Exhibits both the fluxing properties of lithium oxide and the adherence-promoting properties of cobalt oxide. Intercalates lithium ions in battery and cell applications.
Advanced chemistry/technology for primary and secondary batteries. Offers increased performance and twice the energy density of nickel-based batteries. There are several major varieties of lithium ion battery technology, each of which has unique properties. Lithium ion secondary batteries can charge to full capacity in as little as 3 hours.
A variety of lithium ion chemistry/technology that offers high discharge rate capability, long cycle life, and long calendar life.
A variation of lithium ion battery which differs only construction—chemistry is the same. Lithium polymer allows for very flexible packaging, lower cost, and safer operation.
Have the highest specific energy (energy by weight) and energy density (energy by volume) of all primary battery types. Have open circuit voltages (OCVs) between 2.7 and 3.6V. Their relatively high internal impedance limits them mostly to low drain applications.
The discharge current provided by a battery, or drawn by a battery powered device.
A special sensor which ends discharge at a specified voltage level.
Voltage-sensing device to automatically disconnect a battery or cell from a load at predetermined voltage. Low-voltage disconnects prevent cell reversal during discharge.
Method for maintaining the charge of a battery or cell by continuously charging it at a rate sufficient to balance its self-discharge
Generally equivalent to poly batteries and cells in construction, energy density, safety and OCV, though with roughly half the service life. Well-suited to applications with high continuous- or pulse-current requirements due to their lower internal impedance. Available in standard cylindrical and coin styles.
Grouping individual cells within 2% of capacity to prevent cell reversal.
Cells carefully selected by the factory to display within 5% of the same capacity at the time of manufacturer.
Reversible capacity loss found on NiCd and to a lesser extend on NiMH batteries. The modern definition of memory commonly refers to a change in crystalline formation from the desirable small size to a large size.
Phenomenon in which repeated cycling to less than full discharge result in depression in discharge voltage and loss of capacity of the cell Metal Hydride (MH): negative electrode of a battery or cell. Composed of hydrogen-storing Misch metal alloys.
Movement of charged ions under the influence of a potential gradient.
Matrix of the negative electrode of a battery or cell. Composed of hydrogen-storing alloys.
Velocity of ions moving in electrolyte between electrodes of opposite polarity.
Charge termination based on detecting a decrease in voltage which indicates a cell or battery is charged. Designed to terminate charge as over-charge starts.
Electrode in a battery or cell acting as the anode during discharge. Composed of hydrogen-storing alloys. Also called the minus electrode.
Active material used at the positive electrode of the Nickel-cadmium cell.
Battery or cell system comprised of a Nickel (Ni) positive electrode and a metal hydride (MH) electrode.
Mechanical connector used to electrically connect cells in a battery pack
The standard capacity designated by a battery manufacturer to identify a particular cell model.
Average working voltage of a battery or cell. Calculated by multiplying the power (mWh) by the capacity (mAh). (Cell voltages of 1.20 and 1.25 volts are used for NiCd and NiMH batteries.
Potential difference between the electrodes of a battery or cell, measured at the terminals in a no-load condition.
Voltage between the two terminals of the battery without any load.
Over-charge
Forcing of current into a battery or cell after all of its active material has been converted into stored energy.
Discharging a battery or cell after all of its stored energy has been released.
The difference between the actual potential of electro-chemical reaction and the theoretical value at which the reaction becomes balanced.
Process in which oxygen generated at the positive electrode of a battery or cell during over-charge reacts with hydrogen at its negative electrode, producing water.
PBE utilizes a manufacturing technique that produces a high-energy density negative electrode that allows higher capacity for a given cell size and a greatly reduced self discharge.
Interconnecting cells, or batteries with like terminals, are connected to increase the capacity of the resulting battery pack. This resulting battery pack’s capacity is equal to the sum of capacities of the parallel-connected batteries or cells.
Automatic charge termination based on the battery or cell being charged reaching peak voltage. Designed to terminate charge just as over-charge begins.
The charging current which can be continuously maintained, regardless of the state of charge of the cell.
Reversing of polarity of the terminals of a small-capacity cell in a multi-cell battery due to overdischarge.
Obstacles to current flow within NiMH cells.
The term expressing the porous degree of a sintered plate. The equation for its calculation is: Porosity = (V1/V2) x 100. V1 is the volume of pores and V2 is the total volume of the plate including pores.
Electrode of a battery or cell acting as the cathode during discharge. Composed of nickel base (Ni) or nickel hydroxide.
Safety device used in battery packs. At a predetermined temperature threshold, internal resistance goes from a low-resistance state to a high-resistance one to provide over-current and over-temperature protection.
Electrolyte providing ion transport mechanism between the electrodes of NiMH cells.
Energy of an electrical charge, measured by its power to perform work; electro-motive force. Potential energy per unit charge is voltage.
Oxygen gas evolves due to the electrolysis of water in the battery being charged when it reaches a certain potential. This is called the potential of oxygen evolution.
Time rate of energy transfer, measured in Watts (W). Product the voltage (V) across a battery or cell and the current (A) through the battery or cell. W = V x A.
A battery or cell that is not rechargeable and that is disposed of once it has delivered all of its electrical energy.
Cell in a slim, rectangular configuration. Manufactured with rectangular electrodes interspaced by separator sheets.
A high-rate discharge, usually of 1 second or less.
The amount of electric energy supplied to a battery. Its unit is Ah, (ampere-hour).
A method of charge an Nickel-cadmium battery for a short time at a high current level.
Rate of charging a battery or cell to full charge capacity in 2 1/2 to 6 hours.
Amount of milli-amperes (mA) a battery or cell can deliver under specified conditions. Rated capacity is measured at C/5 discharge rate to 1 volt @ 25°C after being charged at C/10 for 16 hours.
Maximum charge/discharge rate of a battery or cell. Expressed in a multiple of the C rate.
See "secondary batteries".
The action by which oxygen gas produced on overcharge is recombined chemically to avoid venting of a sealed cell and loss of water from the electrolyte. See "oxygen recombination".
One or more deep discharge cycles below 1.0 volt/cell ata very low, controlled current. Recondition helps to revert large crystals to small desirable sizes, often restoring the battery to its full capacity.
Reclamation of materials without endangering human health and the environment. Nickel-cadmium cells are fully recyclable.
Resealable vent built into cylindrical and prismatic cells which prevents the build up of high internal pressures.
The capacity remaining in a battery after field use, prior to charge.
The Nickel-cadmium cell is reverse-charged when connected to a charger in the wrong way, and current is forced to flow from the negative to positive electrodes, contrary to the direction of flow during normal charge. Here polarity is reversed, but all electric energy is consumed to generate gas.
Charge method that intersperses discharge pulses between charge pulses to promote the recombination of gases generated during fast charge. Reverse Load charge also helps to reduce memory.
Sealed led acid. An inexpensive secondary battery using lead
A safety mechanism that is activated when the internal gas pressure rises above a normal level. There are two types: Automatically resealable, and unsealable.
A cell which remains closed and does not release either gas or liquid when operated within the limits of charge and temperature specified by the manufacturer. The cell cannot receive addition to the electrolyte.
A battery or cell in which passing electrical current through it in the opposite direction of its discharge can reverse the electro-chemical process, recharging the battery or cell. Commonly called rechargeable batteries.
Loss of energy or capacity in a battery or cell due to internal chemical reactions.
Ion permeable, electrically non-conductive material which electrically separates the positive and negative electrodes of a battery or cell.
Interconnecting cells, or batteries with like un-terminals, are connected to increase the voltage of the resulting battery pack. This resulting battery pack’s voltage is equal to the sum of voltages of the connected batteries or cells in the series.
Under specified conditions, the duration for which a battery or cell can be stored and still retain its performance.
Sintered electrodes were originally developed by Saft and utilized nickel powder to form a highly porous metal sponge. The pores of this material are impregnated with the active material, yielding high discharge performance and very long life.
A thin nickel-plated grid on which nickel powder has been coated.
The plaque on which active materials have been imbedded for charge and discharge reactions.
Typically an over-night charge lasting about 14 hours at a charge current of 0.1C. Battery does not require instant removal when fully charged.
A cell whose voltage rises above its defined boundaries during charging. This voltage rise may be caused by high cell impedance as a result of prolonged battery storage, very cold battery temperature or lack of electrolyte.
The use of cells or batteries in which they are constantly charged so as to be always ready for use.
C/10 charge at 25°C for 16 hours. Sometimes called an overnight charge.
The available capacity of a cell or battery at any given time. Expressed as a percentage of C or its rated capacity.
Ratio of electricity, usually expressed in capacity, remaining in a battery or cell on discharge compared to its rated capacity.
The length of time a cell or battery can be stored on open circuit without permanent deterioration of its performance. Nickel-cadmium cells or batteries can be stored at any state of charge including a fully discharged state.
See "shelf life".
Growth of lead sulfate crystals in SLA batteries which inhibits current flow. Sulfation is caused by storage at low state of charge.
Used almost exclusively in military/aerospace applications. These cells have somewhat lower energy density than manganese dioxide lithium or poly lithium cells. Service life and energy density are generally less than half that of thionyl chloride lithium cells. Require emergency vent structures for safety reasons.
The mechanical lug used to connect cells together to form a battery or to connect it to equipment.
Secondary charge termination at a specified temperature; used in timed, rapid, and fast charge systems.
A one-time, non-resettable fuse used to protect against over-current Thermal runaway — A critical condition arising during constant voltage charging in which the current and the temperature of the battery produce a cumulative mutually-reinforcing effect which further increases them and can lead to the destruction of the battery.
A critical condition arising during constant voltage charging in which the current and the temperature of the battery produce a cumulative mutually-reinforcing effect which further increases them and can lead to the destruction of the battery.
Circuit protection device used to prevent over-current and over-temperature. A thermostat will go from a low-resistance state to an open circuit at a predetermined temperature.
Temperature sensing device, used to measure the temperature of a battery pack or cell. Typically a Negative Temperature Coefficient (NTC) device. Exhibits a predictable and precise decrease in resistance with an increase in temperature.
The area where 3 phases (gas, liquid, and solid) contact with each other, Reactions of substances composing these 3 phases take place easily.
Offer extremely long service life (15 to 20 years) and low self-discharge rates. Ideal for applications with low continuous-current or moderate pulse-current requirements, and applications where physical access is limited. Highest energy density of all lithium types. Manufactured in welded, hermetically sealed cases in cylindrical, coin, and wafer types.
A charging method, terminated after a predetermined amount of time, designed to charge a battery or cell within 6 to 16 hours.
Charge step designed to fully charge a battery or cell when a rapid or fast charge termination that does not reach 100% SOC is used. Most commonly used after a dT/dt termination.
Movement of ions within a cell. Cations carry net-positive charges; anions carry net-negative charges.
See "maintenance charge".
Electronics board which disconnect the load from a battery pack.
During open circuit storage, some battery systems develop a passivation film on the surface of the active material. On the initial discharge, these batteries may momentarily demonstrate a lower than normal voltage until this film is removed by the discharge.
A voltage value a battery is not permitted to rise above on charge and/or fall below on discharge.
A charger that limits the maximum voltage to a battery but allows the current to drop while maintaining the voltage limit. A voltage limiting charge normally also includes current limiting. (Typically used on SLA and Li-ion chargers).
Ratio of a cell's energy to its total volume. Usually expressed in Watt-hours per liter (Wh/l). Also called "power density".
Amount of electric energy that can be withdrawn from a battery or cell under specified conditions. This energy is measured in milli-Watt-hours (mWh). Product of the discharge voltage, discharge rate, and discharge time.
Driving next-gen efficiency and productivity to the battery lifecycle
With soaring demand for batteries today, how can production keep pace? Learn why Vicor power dense modules are perfectly designed to meet today’s demands
Fixed-ratio converters charge up efficiency across battery lifecycle
Power conversion technology limits battery lifecycle productivity. Vicor high-density fixed-ratio converters enable greater efficiency
Fixed-ratio converters unleash innovation across the battery lifecycle
Bidirectional DC-DC converter play a vital role in the evolving battery ecosystem. Learn how high-density power modules are driving new productivity
High-performance power modules drive the battery lifecycle
Learn about the lifecycle of a battery and how high-performance, power dense modules are being used to reduce cost, size and improve efficiency