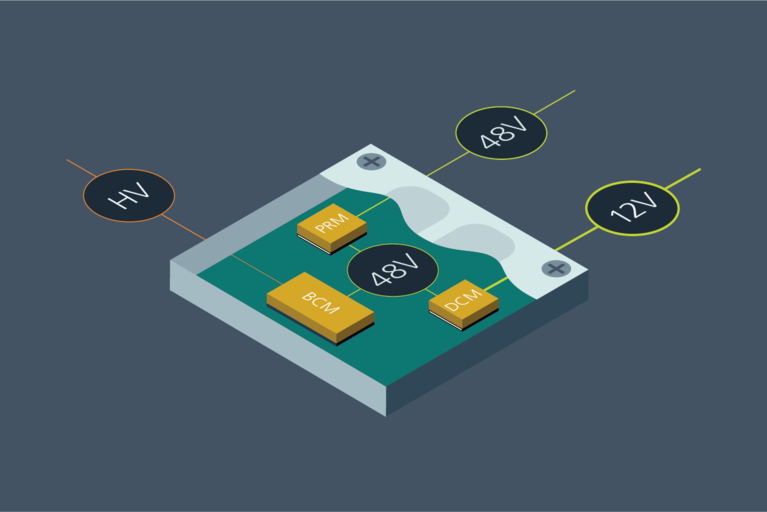
高密度功率模組簡化和縮小電動汽車電源系統設計
Vicor 電源模組為電動汽車應用注入創新。瞭解三款汽車級新產品將如何徹底改變未來的電源設計
The key questions to consider are: How much space do I have on my board? What features do I need? How important is efficiency in my design? When you have established the answers to these questions, you are in a better position to understand what you need to look for when selecting a buck regulator; which elements are essential and which fall into the category “nice to have.”
I apologize if it seems obvious, but it is important to look not just at the package size. So, for example, the graphics below, show two modules available today from two suppliers. The package itself seems quite small, but once you account for the auxiliary devices, primarily capacitors, the overall size of what we call the buck regulation application, increases.
The other thing that can cause the overall solution size to increase is any layout dependency in the design. Specific routing requirements of either analog ground or power output, etc., can increase the size of the design greatly from the package alone.
As I mentioned already, with high power density there are thermal considerations. When you make something smaller, of course, it is more of a challenge to dissipate the heat. Derating is key in looking at what regulator you truly need.
Another consideration is power output. It is not just the size of the one regulator: can you reduce the number of regulators on a board? For example, if you can replace two regulators with just one, that would be a dramatic reduction of space used on the board, improving the density of your solution.
Higher frequency operation is very desirable with regards density. Typically, there is not much of a choice, or you are limited to a frequency range in which the buck regulator operates. However, a buck regulator that operates at a higher frequency will be smaller , and the size of the passives can be reduced. A negative feature of higher frequency operation, though, is switching losses. As you go higher in frequency, you lose on efficiency. This is one of the things we counter in our products through the use of the ZVS topology, but in conventional buck regulators, this is a trade-off that may have to be made.
Some of the more basic features found in today’s buck regulators are soft-start, or tracking.. Soft start allows you to control the ramp up of the output to achieve the final voltage. A similar function is to have the multiple outputs track each other, either one-to-one or in a ratio.If you are powering a microprocessor, you may require the core to come up first before the peripherals, etc. Soft-start and/or tracking are critical to ensure smooth power-up.
Another feature is pre-bias load start-up; this is how well a buck regulator can start up into a rail or power that is already present on the line. Does it pull that line down, or is it able to continue to power from the existing voltage that is on the line to the desired voltage? Pre-biased load start-up ensures that the rail holds at the required voltage when a regulator starts up.
I think efficiency is pretty obvious to people; it is the conversion of the input to the output. What is critical is keeping in mind the efficiency across the operating conditions of the application. Typically, you have efficiency at operating current, that is at a high-load current, and then you also have efficiency when you are in a standby or straight mode; what we call light, or low, load and high load. These two numbers are critical. The light load that is, say, sub one amp is critical for meeting standby requirements. Of course, the high load gives overall efficiency while in full operation.
While device efficiency is the measurement of the output to the input, any calculation of system efficiency needs to take into account line losses. Line losses can play a very important role, when looking at overall efficiency. Part of the whole concept of Point-of-Load conversion is the idea to reduce the line losses by placing regulation near the point of load. This can be done by routing a higher voltage closer to the point of load and then regulating down to a lower voltage. By bearing these performance criteria in mind, you can design an efficient, effective buck regulator to suit your application size and needs.
In the next part of the interview, we will look at some of the ways buck regulators can be implemented and then we will consider the role of Zero Voltage Switching (ZVS) architecture.
Related content
高密度功率模組簡化和縮小電動汽車電源系統設計
Vicor 電源模組為電動汽車應用注入創新。瞭解三款汽車級新產品將如何徹底改變未來的電源設計
高密度電源模組推動主動懸架技術日趨成熟
主動懸掛系統已從 20 世紀 90 年代的測試版發展成為今天的 48V 驅動系統。瞭解電源模組對電源系統設計的影響
先進的電源模組封裝優化了自動駕駛電動巴士的可用功率、可靠性和安全性
Vicor 的高效電源模組確保最少的散熱,降低對複雜冷卻解決方案的需求,並最大限度地提升功率輸出
基於 MHz 開關頻率的器件助力實現 DC-DC 轉換器和 EMI 濾波器的小型化
想像一下,使用 DC-DC 轉換器解決方案來利用高頻開關的優勢,而不會發生傳統解決方案的缺點