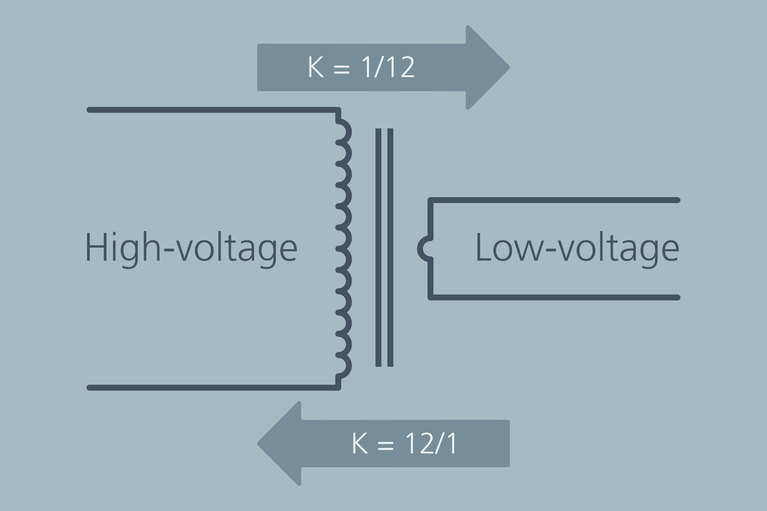
Power delivery to the various points‑of‑load within a system is done via a Power Delivery Network, commonly referred to as the PDN. The PDN consists of cables, bus bars, connectors, circuit board copper power planes, power converters and regulators. The performance of a PDN is measured in terms of power loss, size, weight and cost. Governing PDN performance is its overall architecture, such as the use of AC or DC voltage distribution, specific voltage levels and when and how many times the network needs voltage conversion and regulation. This white paper discusses a particular type of DC‑DC converter, the fixed‑ratio converter (sometimes referred to as a bus converter), and why power system designers should consider it an essential part of the power delivery architecture, particularly for high‑power systems.